Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Agrivoltaic system modeling#
Irradiance at crop level between rows
This example demonstrates how to calculate power output for a bifacial agriPV plant as well as calculating the irradiance at crop level using pvlib’s infinite sheds model. For an overview of agrivPV concepts and performance, the reader is referred to DOI: 10.69766/XAEU5008.
This gallery example is based on an actual AgriPV plant, namely European Energy’s Flakkebjerg AgriPV site.
The first steps are to define the plant location and to calculate solar position and clearsky irradiance for a single day as an example.

Photo of an agriPV system. Source: Adam R. Jensen#
import pvlib
import pandas as pd
from pvlib.tools import cosd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
location = pvlib.location.Location(latitude=55, longitude=10)
times = pd.date_range('2020-06-28', periods=24*60, freq='1min', tz='UTC')
solpos = location.get_solarposition(times)
clearsky = location.get_clearsky(times, model='ineichen')
Next, we need to define the plant layout:
height = 2.6 # [m] height of torque above ground
pitch = 12 # [m] row spacing
row_width = 2 * 2.384 # [m] two modules in portrait, each 2 m long
gcr = row_width / pitch # ground coverage ratio [unitless]
axis_azimuth = 0 # [degrees] north-south tracking axis
max_angle = 55 # [degrees] maximum rotation angle
Before running the infinite sheds model, we need to know the orientation of the trackers. For a single-axis tracker, this can be calculated as:
tracking_orientations = pvlib.tracking.singleaxis(
apparent_zenith=solpos['apparent_zenith'],
solar_azimuth=solpos['azimuth'],
axis_azimuth=axis_azimuth,
max_angle=max_angle,
backtrack=True,
gcr=gcr,
)
For agrivPV systems, the local albedo is dependent on crop growth and thus changes throughout the seasons. In this example, we only simulate one day and thus use a constant value. Similarly, we will assume a constant air temperature to avoid getting external data. Both albedo and air temperature could be defined as Series with the same index as used for the solar position calculations.
Now, we are ready to calculate the front and rear-side irradiance using the pvlib infinite sheds model.
dni_extra = pvlib.irradiance.get_extra_radiation(times)
irradiance = pvlib.bifacial.infinite_sheds.get_irradiance(
surface_tilt=tracking_orientations['surface_tilt'],
surface_azimuth=tracking_orientations['surface_azimuth'],
solar_zenith=solpos['apparent_zenith'],
solar_azimuth=solpos['azimuth'],
gcr=gcr,
height=height,
pitch=pitch,
ghi=clearsky['ghi'],
dhi=clearsky['dhi'],
dni=clearsky['dni'],
albedo=albedo,
model='haydavies',
dni_extra=dni_extra,
bifaciality=0.7, # [unitless] rear-side power relative to front-side
)
Once the in-plane irradiance is known, we can estimate the PV array power. For simplicity, we use the PVWatts model:
N_modules = 1512 # [unitless] Number of modules
pdc0_per_module = 660 # [W] STC rating
pdc0 = pdc0_per_module * N_modules
gamma_pdc = -0.004 # [1/degrees C]
temp_cell = pvlib.temperature.faiman(
poa_global=irradiance['poa_global'],
temp_air=temp_air,
)
power_dc = pvlib.pvsystem.pvwatts_dc(
effective_irradiance=irradiance['poa_global'],
temp_cell=temp_cell,
pdc0=pdc0,
gamma_pdc=gamma_pdc)
power_dc.divide(1000).plot()
plt.ylabel('DC power [kW]')
plt.show()
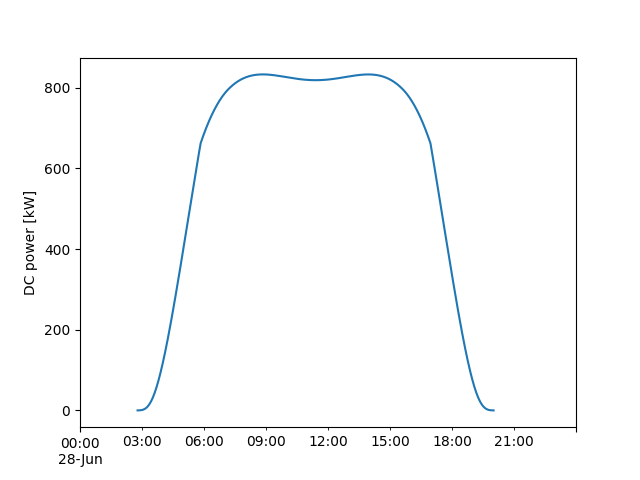
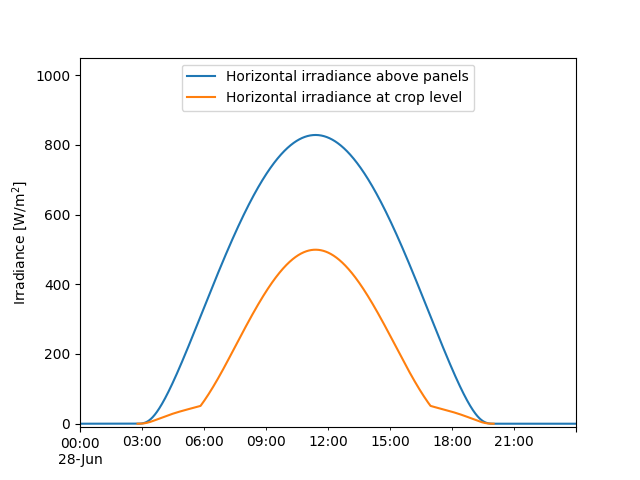
In addition to the power output of the PV array, we are also interested in how much irradiance reaches the crops under the array. In this case we calculate the average irradiance on the ground between two rows, using the infinite sheds utility functions.
This consists of two parts. First we determine the diffuse irradiance on ground and second we calculate the fraction of the ground that is unshaded (i.e., receives DNI).
vf_ground_sky = pvlib.bifacial.utils.vf_ground_sky_2d_integ(
surface_tilt=tracking_orientations['surface_tilt'],
gcr=gcr,
height=height,
pitch=pitch,
)
unshaded_ground_fraction = pvlib.bifacial.utils._unshaded_ground_fraction(
surface_tilt=tracking_orientations['surface_tilt'],
surface_azimuth=tracking_orientations['surface_azimuth'],
solar_zenith=solpos['apparent_zenith'],
solar_azimuth=solpos['azimuth'],
gcr=gcr,
)
crop_avg_irradiance = (unshaded_ground_fraction * clearsky['dni']
* cosd(solpos['apparent_zenith'])
+ vf_ground_sky * clearsky['dhi'])
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
clearsky['ghi'].plot(ax=ax, label='Horizontal irradiance above panels')
crop_avg_irradiance.plot(ax=ax, label='Horizontal irradiance at crop level')
ax.legend(loc='upper center')
ax.set_ylabel('Irradiance [W/m$^2$]')
ax.set_ylim(-10, 1050)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.816 seconds)
